In an age where technology permeates every aspect of our lives, facial recognition has emerged as a pivotal tool for identification and security. Traditionally reliant on 2D images, facial recognition systems have made significant strides, but they still face challenges in accuracy and reliability. The introduction of 3D scanning technology is revolutionizing this field, offering enhanced precision and new applications that were previously unimaginable.
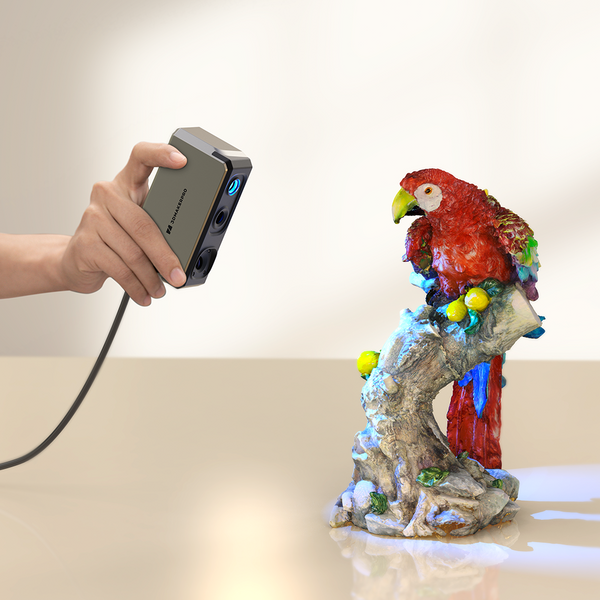
In this blog, we will explore the distinct working mode between facial recognition and 3D scanning, the advantages and applications of 3D scanning, and the potential for their integration to drive significant advancements. We will also provide practical tips to enhance your experience with face scanning using the Mole and Seal scanners from 3DMakerpro.
The Basics of Facial Recognition
Facial recognition is a technology that identifies individuals by comparing their faces to stored images or videos. This process involves capturing facial features and converting them into a set of digital data, which is then stored in a database. When a match is needed, the system compares the new digital information against the stored data to verify consistency. While effective, traditional 2D systems have limitations, particularly in varying lighting conditions and angles.

The Shift to 3D Scanning Technology
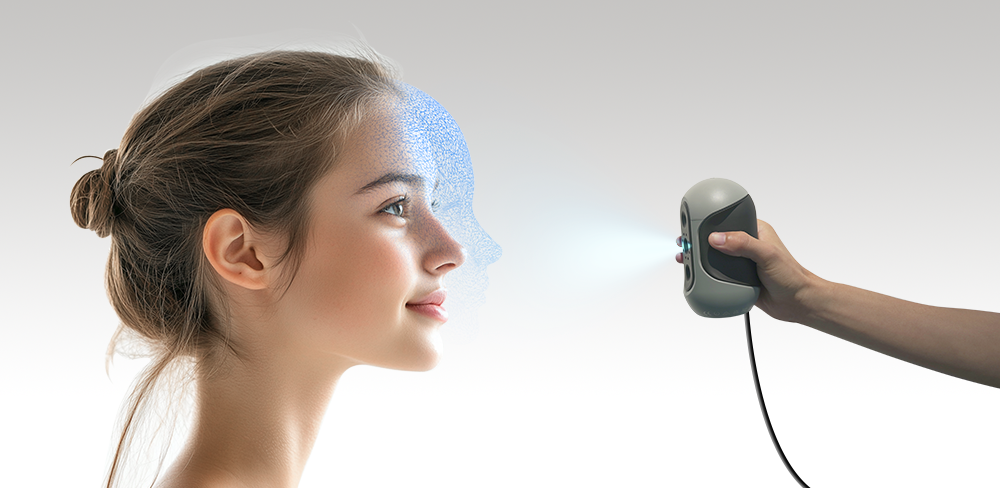
3D scanning technology captures the intricate three-dimensional details of a face, providing a far richer dataset than 2D scanning. Utilizing methods such as laser scanning, structured light, or photogrammetry, 3D scanners create a detailed point cloud representation of the face. This data is then translated into a digital model, which can be analyzed for more accurate identification.
Advantages of 3D Scanning
① Increased Accuracy
3D scanning captures depth and contour, making it more reliable for identifying individuals, even in challenging conditions.
② Robustness to Variability
Unlike 2D images, which can be affected by lighting or facial expressions, 3D models maintain their integrity across various conditions.
③ Enhanced Applications
The detailed data from 3D scans opens doors to new applications in industries such as healthcare, entertainment, and security.
Applications of 3D Scanning in Facial Recognition

a) Security and Surveillance
Enhanced accuracy in identifying individuals can improve security measures in public spaces, airports, and restricted areas.
b) Promote Consumption
In retail, 3D scanning can be used for personalized marketing and customer engagement by creating tailored experiences based on individual characteristics. Additionally, face-scanning payment systems bring convenience to consumers and stimulate growth in consumption, benefiting businesses.
c) Healthcare Innovations
In medical fields, 3D facial scanning can assist in planning surgeries, creating prosthetics, and even in orthodontics for custom dental solutions.
d) Forensics Evidence
In forensics, 3D facial scanning accurately captures evidence from crime scenes and the facial characteristics of victims, aiding investigations and helping to uncover the truth.
e) Entertainment and Gaming
3D scanning technology can copy and recreate the lifelike characters and environments in movies and video games, allowing for a more immersive experience.
Addressing Concerns
Despite its advantages, the rise of facial recognition technology, especially when combined with 3D scanning, raises questions about privacy and security. Concerns about data misuse and accuracy compared to other biometric methods—such as iris or fingerprint recognition—are valid. However, the integration of 3D scanning can help mitigate these issues by enhancing the accuracy of identification and providing more robust data points for verification.
Scanning Tips
①Geometry mode
We recommend using Geometry scanning mode to enhance scanning speed and fluidity.
② Slow Movement speed
A slower scanning speed ensures high-quality data capture and helps eliminate misalignment issues.
③ Appropriate distance
Please pay close attention to the prompts in the left window regarding scanning distance. Maintaining the correct distance is crucial for a successful scan—avoid being too close or too far away.
④ Avoid eye contact
To protect the eyes of the person being scanned, please refrain from looking directly at the scanner, as its light can be harsh. Instead, direct your gaze slightly below the line of sight. Be aware that fine textures, such as eyebrows and hair, may not be accurately represented in the scan images.
Mole Scans Face
Seal Scans Face
Conclusion
The transition from 2D to 3D scanning technology is transforming the landscape of facial recognition. By leveraging the strengths of 3D scanning, we can achieve greater accuracy and reliability, paving the way for innovative applications across various sectors. As technology continues to evolve, embracing these advancements will help us create a more secure, efficient, and personalized world. The future of facial recognition is bright, and with 3D scanning leading the charge, we are only beginning to scratch the surface of its potential.