In recent years, the intersection of technology and archaeology has transformed our approach to studying ancient life. Among these advancements, Toucan 3D scanner stands out as a revolutionary tool for examining prehistoric tortoises and other creatures that once roamed the Earth. This technology unlocks a treasure trove of information, providing invaluable insights into the lives of these remarkable beings and the ecosystems they inhabit.
The Significance of Scanning Prehistoric Giant Tortoises
Prehistoric giant tortoises, such as those of the genus Meiolania, provide invaluable insights into the evolution of reptiles and the environmental conditions of past eras. These enormous creatures, which could grow to the size of small cars, not only represent remarkable biological adaptations but also serve as indicators of ancient climates and ecosystems.
Studying the anatomy of these tortoises reveals crucial details about their diets, behaviors, and interactions with other species. For instance, their massive shells and robust structures suggest they were well-adapted to their environments, providing clues about their herbivorous diets and the flora available at the time. Moreover, analyzing these fossils can help scientists better understand the patterns of extinction that have shaped our planet's biodiversity, particularly because many extinct species serve as a stark reminder of the delicate balance within ecosystems.
By examining the remains of prehistoric tortoises through 3D scanning, researchers can not only piece together their biological puzzle but also make connections to current environmental challenges, highlighting the importance of conservation and the repercussions of climate change on biodiversity.
Drawbacks of Traditional Scanning Methods
Historically, traditional methods of studying fossils involved physical handling and manual documentation, typically through photography and basic imaging techniques. While these methods have provided a foundation for paleontological research, they come with significant limitations:
Physical Deterioration
Handling delicate fossils can lead to wear and tear, risking the loss of irreplaceable details. Fossils are often fragile, making them more susceptible to damage with each interaction.
Limited Detail
Conventional imaging techniques may fail to capture the intricate details of a specimen, such as fine anatomical features and textures. This lack of detail can hinder accurate analysis and interpretation.
Accessibility Issues
Traditional methods often require the fossil to be physically present for study, limiting access for researchers who may be located far from the specimen's site, thereby slowing down collaborative research efforts.
Static Documentation
Traditional photographs and drawings don’t allow for interactive exploration of the morphology. Once documented, the information is fixed and cannot be easily manipulated or analyzed anew.
Advantages of Modern 3D Scanning
The advent of 3D scanning technology has transformed our ability to study prehistoric tortoises, providing solutions to many constraints of traditional methods. Here are some of the key advantages:
Precision and Detail
Modern 3D scanning captures minute details and textures of fossils with remarkable accuracy, allowing researchers to delve deeply into the intricacies of ancient anatomy. High-resolution scans not only preserve the overall shape of a tortoise's shell but also reveal subtle features, such as the unique patterns and textures that characterize its surface. This level of detail provides a comprehensive understanding of the tortoise's biology, enabling scientists to analyze its structure—specifically, how its physical traits might have contributed to its survival in ancient environments.
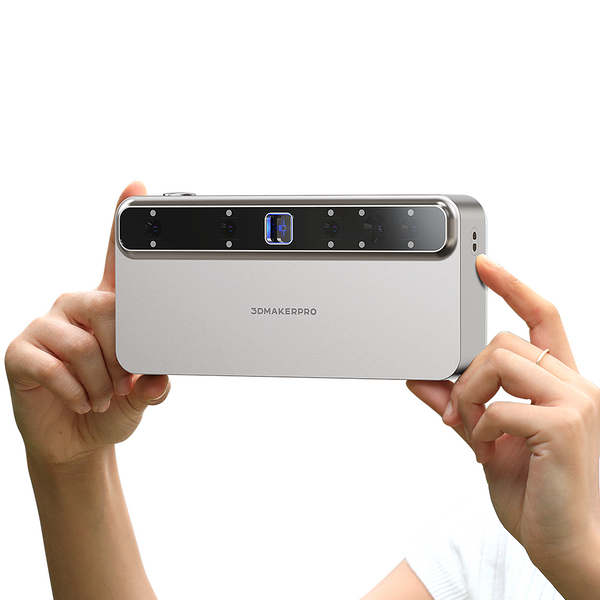
The Toucan 3D Scanner exemplifies this precision, featuring four 3D cameras and a 48 MP RGB camera, which collectively enhance the scanning process. Its single-frame accuracy reaches ≤ 0.03mm for small objects and ≤ 0.10mm for larger specimens, ensuring that even the most delicate fossils are captured with fidelity. Furthermore, its exceptional resolution—≤ 0.03mm for fixed shots and ≤ 0.05mm and ≤ 0.10mm for small and large objects, respectively—makes it an invaluable tool for researchers working with fragile specimens.
What sets the Toucan apart is its dual-lens imaging technology, which combines seven photos into a single frame of point cloud data. This innovative approach significantly improves the scanner's ability to capture thin and small objects with enhanced clarity, providing detailed insights that traditional single-frame coded scanners often miss. By harnessing these advanced capabilities, researchers can achieve a level of detail that greatly enriches our understanding of prehistoric life.
Non-invasive Preservation
One of the most significant advantages of 3D scanning technology is its non-invasive nature, a stark contrast to traditional methods that often involve physical handling of fossils. This innovative approach eliminates the risk of deterioration and damage to original specimens, ensuring that these invaluable artifacts remain intact for future research and analysis. By preserving the pristine condition of these fossils, 3D scanning allows scientists to study them repeatedly without the wear and tear that can arise from physical interactions.
The Toucan 3D Scanner employs a blue laser structured light source (Class 1/Class 3R), which is designed to be safe for human eyes, further enhancing its suitability for delicate scientific environments. This non-contact scanning method meticulously captures detailed images of fossils without putting them at risk. As a result, fossils can be protected and preserved with the utmost care, providing researchers with reliable, high-quality data for their studies. Furthermore, the Toucan 3D Scanner allows for continuous handheld scanning, enabling scientists to capture complex shapes and features of prehistoric tortoises from multiple angles. This flexibility not only enriches the data collected but also fosters a more comprehensive understanding of these extraordinary ancient creatures while ensuring their preservation for generations to come.
Global Collaboration
The digital models generated through 3D scanning technology enable seamless sharing across geographical boundaries, fundamentally transforming the landscape of scientific collaboration. This enhanced accessibility allows researchers from around the world to engage in joint studies, analyze specimens, and exchange insights without the constraints of physical presence at the excavation site or laboratory.
Tools like JM Studio facilitate this collaborative environment by allowing users to view, manipulate, and make simple adjustments to 3D models freely. This versatility empowers researchers to tailor their analyses according to their specific needs and preferences, fostering a more interactive engagement with the data.
Interactive and Engaging
For school education, the digitization of fossils through 3D scanning is revolutionizing school education by introducing interactive exploration of ancient specimens. Students can rotate, zoom, and manipulate 3D models, uncovering intricate details that traditional static images often obscure. This hands-on engagement fosters a deeper understanding of paleontology, making learning not only more dynamic but also more memorable. By integrating these digital tools into classroom curricula, educators can ignite curiosity in young minds, encouraging them to delve into the wonders of ancient life and the scientific principles that govern it.
For public education, interactive 3D models are transforming how the general audience engages with paleontological exhibits. Museums can seamlessly integrate these models into their displays, allowing visitors to explore fossils interactively, which enhances their overall experience. Moreover, the ability to access these models online extends educational opportunities beyond museum walls, making complex scientific concepts more approachable and understandable for everyone. By turning fossil displays into immersive learning experiences, public institutions can inspire greater interest in science, conservation, and the history of life on Earth, ultimately cultivating a more informed and curious community.
For Scientific Researchers, the digitization of fossils provides unprecedented opportunities for enhanced analysis and collaboration. The ability to manipulate 3D models allows scientists to examine specimens in detail, revealing features that may be missed through traditional methods. This technology facilitates collaborative research efforts, enabling experts from various fields to share insights and findings without the need for physical presence at a site. Additionally, exporting 3D models to virtual reality platforms expands research possibilities, allowing scientists to immerse themselves in simulated environments. This innovative approach transforms how researchers visualize and study fossils, paving the way for new discoveries and a deeper understanding of prehistoric life.
Facilitating Replication and Preservation
3D scanning enables the creation of highly accurate replicas of fossils, which serve a multitude of purposes, including research, education, and museum displays. These detailed replicas ensure that original specimens are preserved and protected while still allowing for extensive study and exploration. By providing researchers and educators with access to precise copies, 3D scanning helps maintain the integrity of invaluable artifacts, facilitating ongoing investigation and knowledge sharing without compromising the safety of the originals.
Furthermore, the online preservation of these digital models allows them to be stored indefinitely, making them accessible to anyone with a smartphone, computer, or internet connection. This aspect fosters inclusivity, as individuals who may not have the opportunity to visit museums can still experience the wonders of ancient life. The digital archives serve as lasting memories, ensuring that the stories and significance of these fossils are shared widely and appreciated by the broader community, not just those who physically encounter them in museum settings. In this way, 3D scanning not only advances scientific research but also democratizes access to knowledge about our planet's rich geological history.
In A Word
The revival of ancient giant tortoises through 3D scanning goes beyond scientific curiosity; it reveals the intricate web of life from millions of years ago and underscores the importance of safeguarding our modern ecosystems. By uncovering details about these prehistoric tortoises, researchers gain valuable insights into their evolutionary adaptations and the environments they once inhabited.
As we embrace modern 3D scanning technology, we overcome the limitations of traditional methods, preserving fossils while enhancing collaborative research and public engagement. The story of these tortoises serves as a poignant reminder of life's fragility and the ongoing impact of environmental changes. By learning from these ancient beings, we are better equipped to tackle today's urgent ecological challenges, ultimately empowering us to protect the biodiversity that sustains our planet for the future.