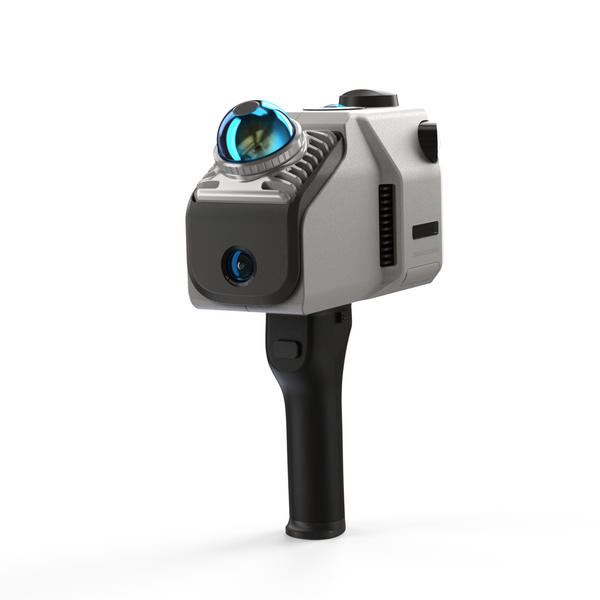
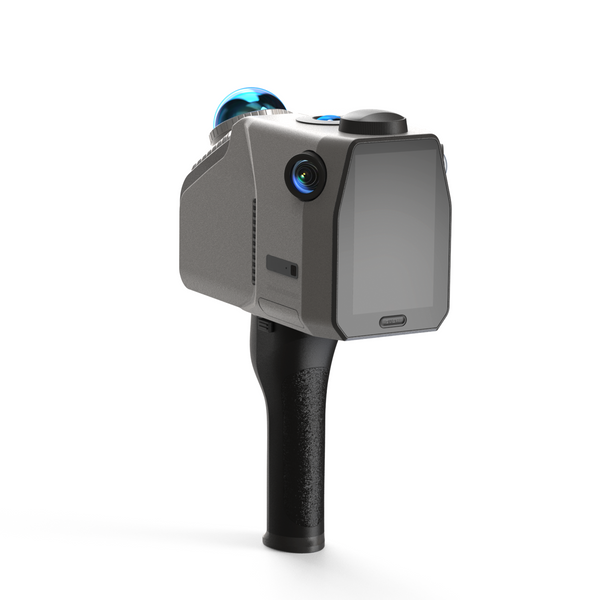
In recent years, smartphone technology has made 3D scanning more accessible, with many phones equipped with advanced cameras and sensors that allow users to easily capture 3D images. However, the imaging quality often falls short of that offered by professional tools, as smartphones rely on algorithms that can introduce errors. Professional 3D scanners are designed to capture intricate details and provide higher accuracy and fidelity, making them ideal for industries such as architecture, engineering, and healthcare. 3D scanners can be categorized into various types, including Laser Scanners, Structured Light Scanners, Contact Scanners, Photogrammetry, Time-of-Flight Scanners, and Optical Scanners. In this comparison, we will explore their respective advantages and disadvantages to help you choose the scanning method that best suits your needs.

Operation Method Comparison
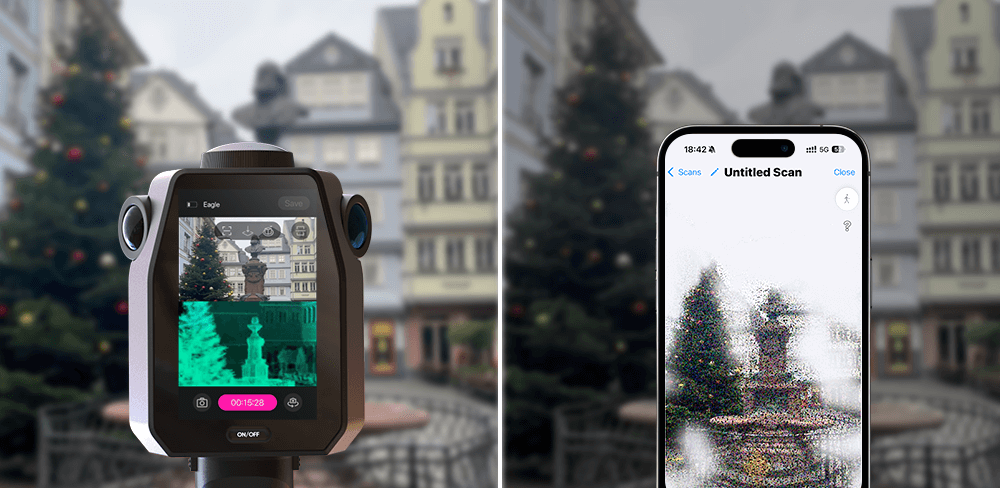
3D scanning with phones is straightforward. Simply open the scanning app (e.g., Qlone, 3D Scanner App, Trnio, Snapchat Lens Studio, Scandy Pro), select the appropriate mode, and rotate the object at each marked horizontal plane to ensure all points are captured. If the scan is not complete, you may need to make several passes.
In contrast, using a professional scanner usually requires connecting it to a computer and a turntable. For example, the Moose scanner allows you to scan an object from multiple angles—front, side, and bottom—typically taking one to five minutes. More complex objects may require additional adjustments and trial and error, but the final image is often complete and clear, accurately restoring the object's color.
In Accuracy Aspect
Smartphones capture images using their built-in cameras and sensors, processing multiple 2D images through algorithms to reconstruct them into a 3D model. Depth is typically estimated using structured light or depth-sensing technology, such as LiDAR in some models. Smartphone scanning accuracy usually ranges from ±1 mm to ±5 mm.
On the other hand, structured light scanners, like phase shift scanners, project patterns onto an object's surface and analyze the reflected light to calculate depth information. For example, the Toucan 3D Scanner employs high-power MEMS optics and a blue laser structured light source, utilizing a dual-lens imaging system that combines seven images into a single point cloud frame. This design enhances accuracy, particularly for thin and small objects, achieving impressive single-frame accuracy of ≤ 0.03 mm for small items and ≤ 0.10 mm for larger ones.
In Speed Aspect
The scanning speed of smartphone apps can vary significantly based on the application and device. Generally, smartphone 3D scanning apps can capture scans at speeds ranging from 1 to 10 frames per second (fps). However, the overall scanning time also depends on the complexity of the object and the scanning method. Users might typically spend around 1 to 5 minutes per object when they 3D scan with a phone, while scanning larger spaces may take 15 minutes or more. Additional time may be needed for processing the data into a usable 3D model, which can take several minutes to an hour, depending on the app and device's processing capabilities.
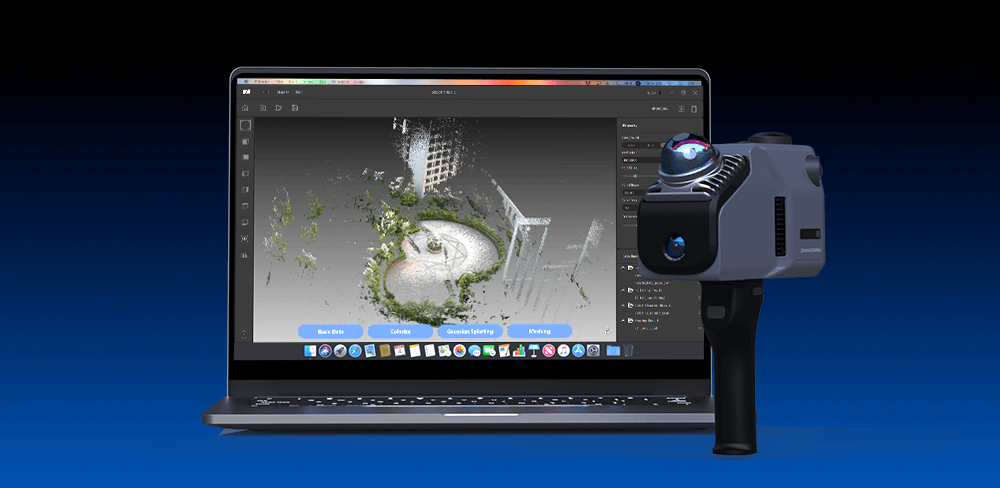
While Eagle LiDAR scanner offers a scanning radius of up to 70 meters under 80% reflectivity conditions. It efficiently models large city blocks in just 5 to 10 minutes, boasting a 360° x 59° field of view—30% greater coverage than standard products. With a simple rotation, it can capture a panoramic view of an entire room and collects up to 200,000 points per second, maintaining data quality even at speeds of 20 km/h. However, converting the data into a colored point cloud or Gaussian splatter may take more than ten minutes or even over an hour, depending on the complexity of the scanned data.
In Professionalism Aspect
Professional Aspects: Mobile scanning offers numerous advantages, such as capturing key features, taking measurements, and generating 3D models. With just a smartphone and an app, users can scan anytime, anywhere. While scan types vary, images can be incomplete and detailed post-processing (such as model modification and noise reduction) is not possible.
In contrast, different 3D scanners can cater to specific needs. For medium-sized objects, the Moose scanner offers an accuracy of 0.03 mm. The Toucan 3D Scanner is ideal for scanning dark objects, as its phase-shift technology is less affected by lighting conditions. For generating spatial models, the Eagle LiDAR Scanner excels in both indoor and outdoor environments. Each of these scanners is highly specialized, excelling in its own area of expertise.
In User Experience Aspect
3D scanning with phones is convenient and can be used anytime, anywhere. Simply download the app and start using it. However, the device may get hot after prolonged use. Some apps require payment, making it less user-friendly for novice users. Some apps also require account creation and login, which may not be cost-effective for privacy-conscious users or those who don't plan to use the app long-term.
3DMakerpro's professional 3D scanner comes with free access to JM Studio and Ray Studio, which can handle most model post-processing issues. New users can also use Guest Mode. The 3D scanner also features a built-in fan for cooling, eliminating the need to worry about burning out. The scanner can be connected to a computer for desktop scanning, a mobile phone for handheld scanning, or an automatic turntable for hands-free scanning. This makes the user experience more efficient and convenient. After scanning, you can even export it to a format supported by slicing software for 3D printing. In this way, your scanned 3D model will be vividly presented in front of you, rather than just a virtual cold 3D image.
In summary, 3D scanning with phones offers the convenience and ease of use that makes it suitable for everyday applications, while professional 3D scanning provides exceptional accuracy and detail, which is crucial for industrial and professional fields. Choosing between the two depends on your specific needs, budget, and the level of accuracy required for the task at hand.