3D Models
Crime Scene Reconstruction
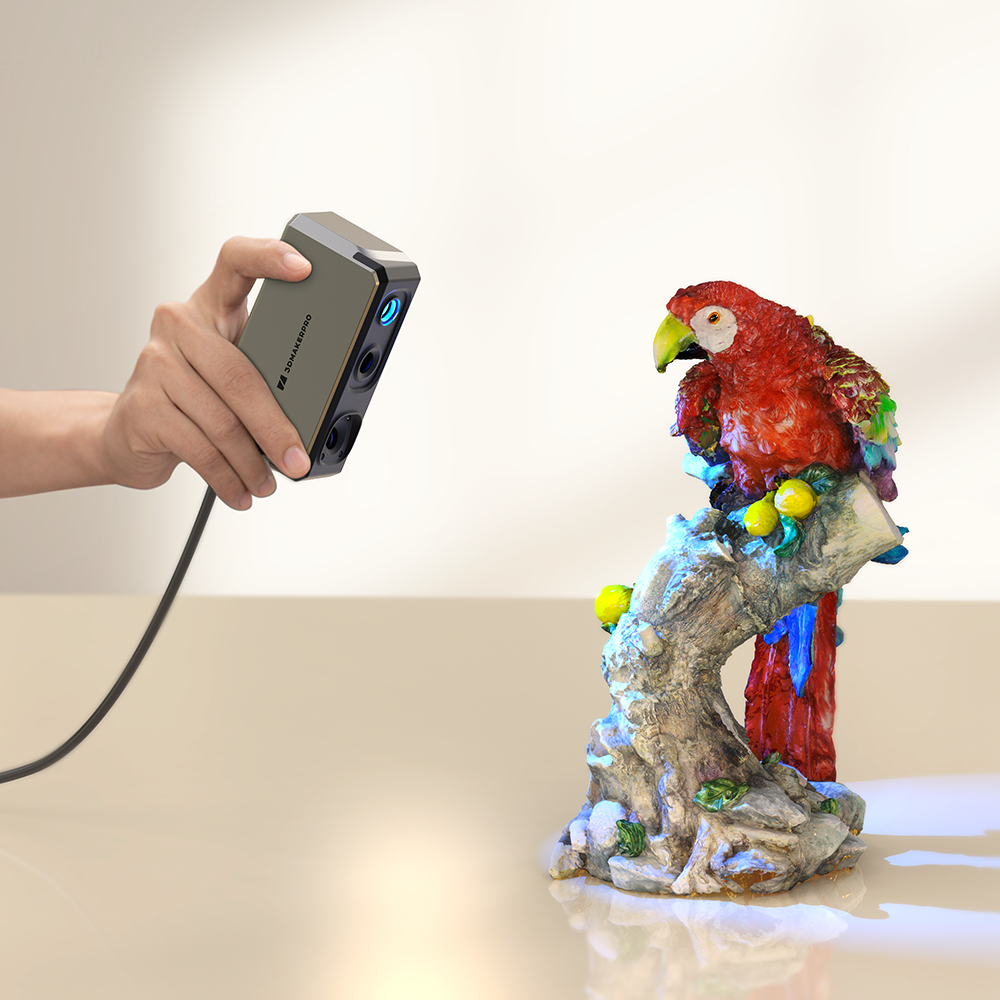
One of the primary forensic applications of 3D scanning is crime scene reconstruction. By capturing the entire scene in three dimensions, investigators can visualize the spatial relationships between objects, which is crucial for understanding how a crime occurred. This digital map can be integrated into virtual reality simulations, immersing juries and investigators in the environment at the time of the crime. Such immersive experiences significantly enhance comprehension of complex scenes, making it easier for participants in legal proceedings to grasp the details. The Whale scanner, equipped with dual cores, can even efficiently scan black objects, assisting forensic professionals in accurately recording evidence.

Evidence Documentation
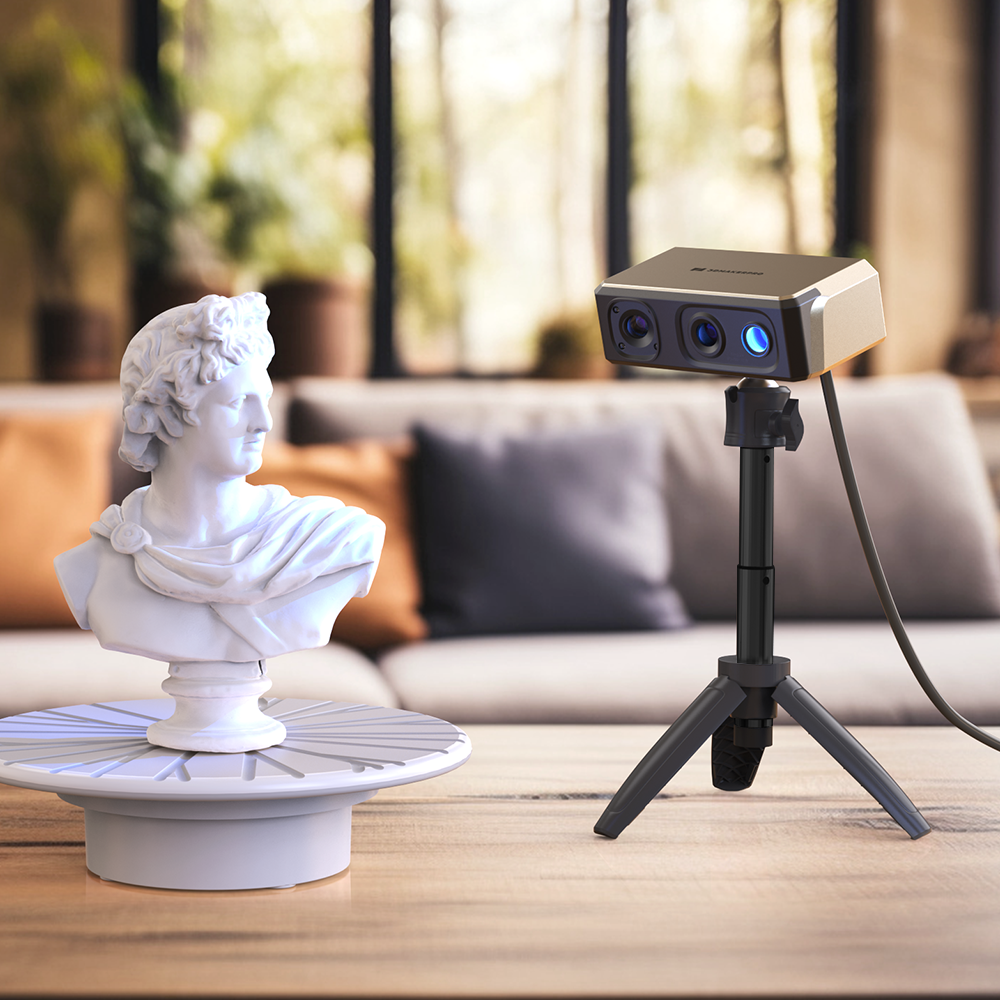
In addition to reconstruction, 3D scanners play a critical role in evidence documentation. They provide a permanent digital record of the crime scene, preserving details that might otherwise be lost over time. This meticulous documentation is particularly important for fragile evidence, such as biological samples or fingerprints, which can degrade or change. The precision of 3D scans, such as those from the Seal scanner with 0.01 mm accuracy, allows forensic experts to analyze and measure evidence accurately, leading to more informed conclusions about its significance and relevance.
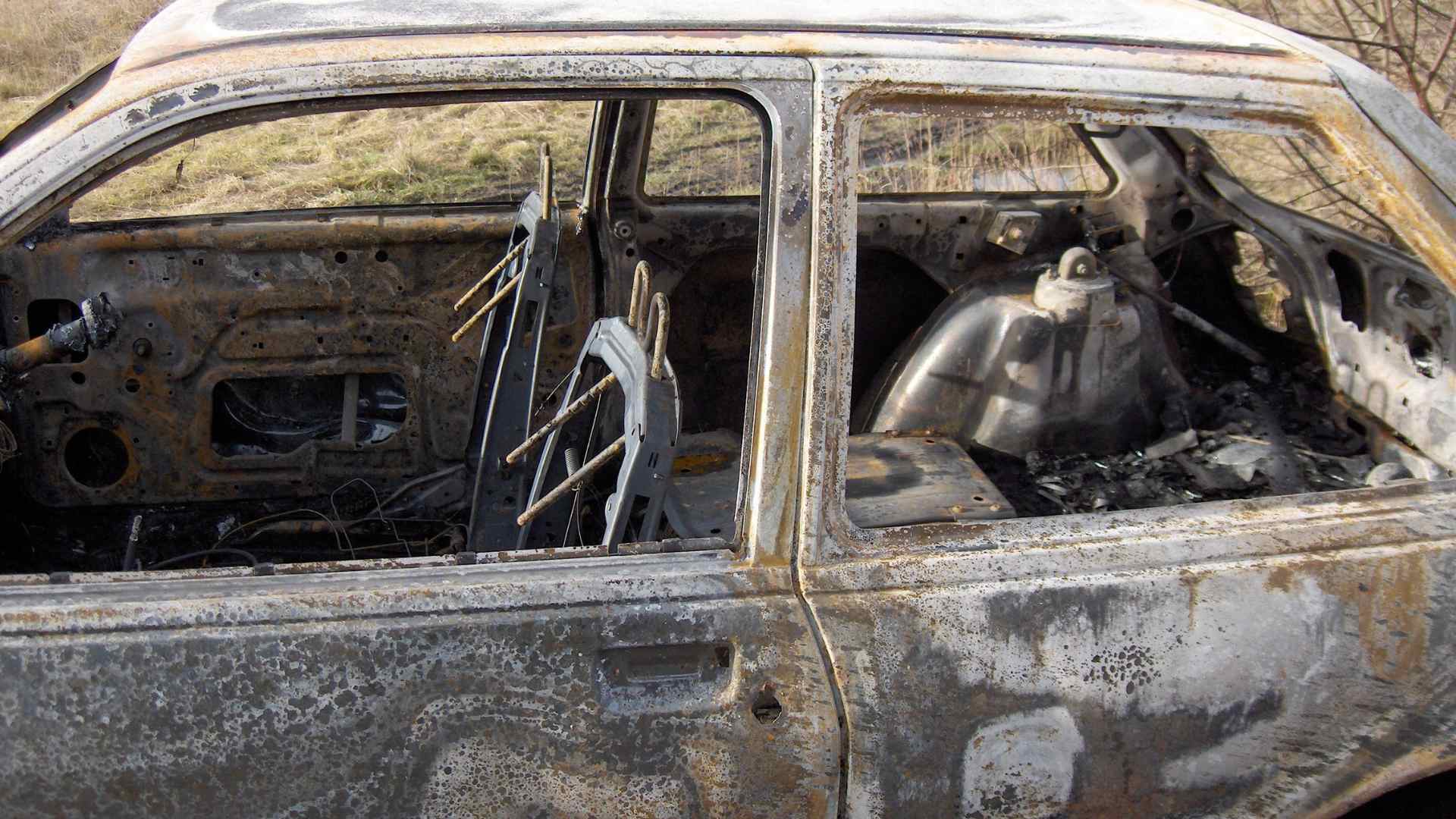
Accident Reconstruction
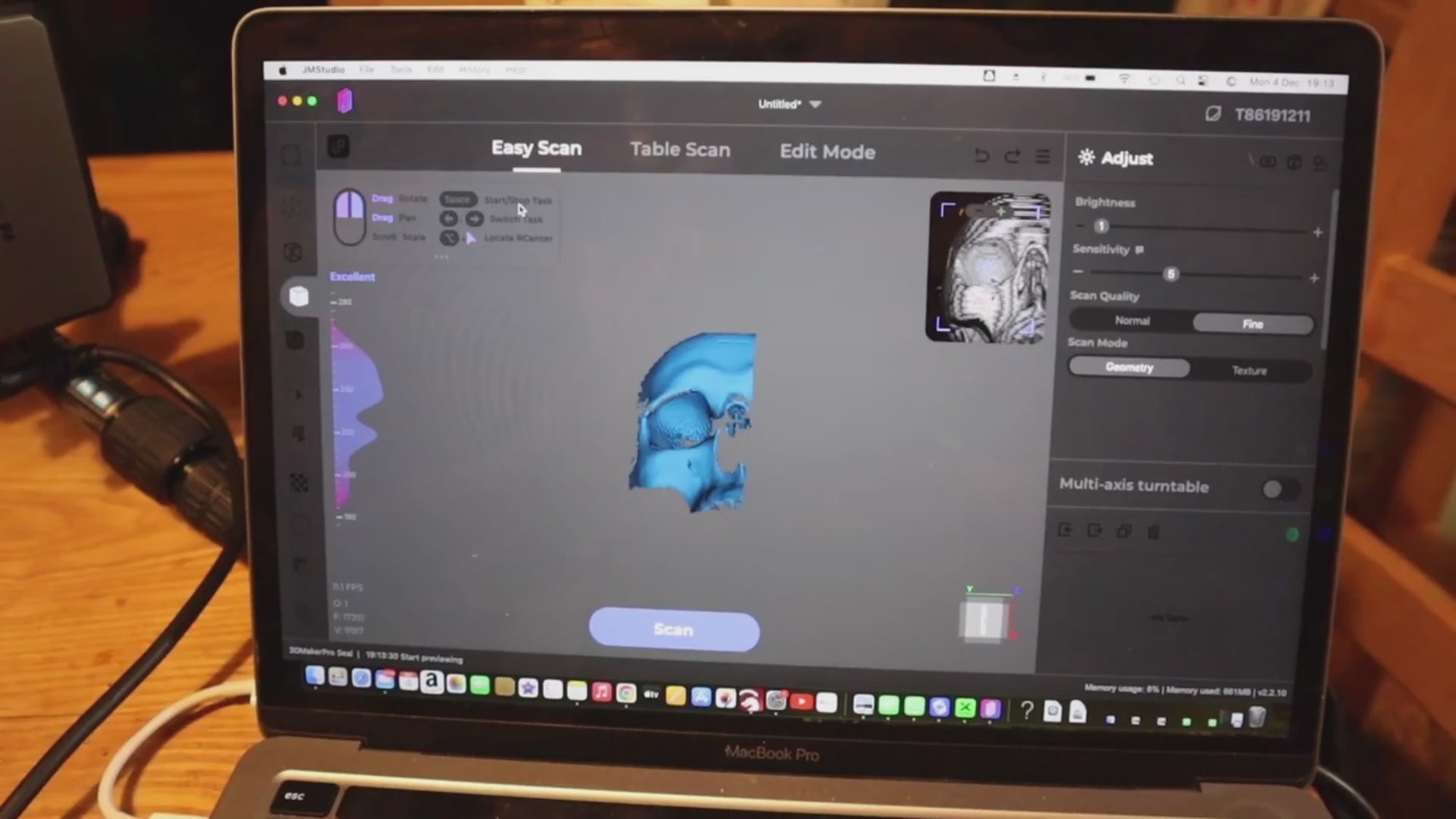
Another significant application of 3D scanning is in accident reconstruction. In vehicular incidents, 3D scanners can capture the positioning of vehicles, road conditions, and other environmental factors essential for understanding the dynamics of the accident. For instance, the Whale scanner, with a frame rate of 10 fps, offers a wide-core capture range of 530 x 390 mm and a micro-core capture range of 200 x 100 mm, making it easier to work in outdoor settings. By analyzing these digital models, forensic engineers can determine critical details like impact angles and speeds, which are vital for establishing liability and understanding the circumstances surrounding the event. This data can also be used to create simulations that explore various scenarios, further clarifying the sequence of events.
Whale Scanner V.S. Seal Scanner




0.10mm (wide-core)
0.05mm (micro-core)
0.01mm
0.50mm (wide-core)
0.20mm (micro-core)
0.05mm
530*390mm (wide-core)
200*100mm (micro-core)
10-300mm
Automatic matching
Visual tracking
650±250mm (wide-core)
300±100mm (micro-core)
180-280mm
530×370mm (wide-core)
200×100mm (micro-core)
100x75mm
NIR
Blue light
Support
Support
230×148×188mm
110×60×35mm
≤1500g
254g
Success Stories 1
REVIEW: Whale 3D Scanner | Click 3D Ep. 60 | 3D Scanning | 3D Forensics | CSI

Success Stories 2
Seal's Head Sculpture 3D Scan | 3DMakerpro Seal #3dscanning #3dprinting #3dmakerpro

Success Stories 3
3DMakerpro Whale Motorcycle Scan Challenge

Recommend Products
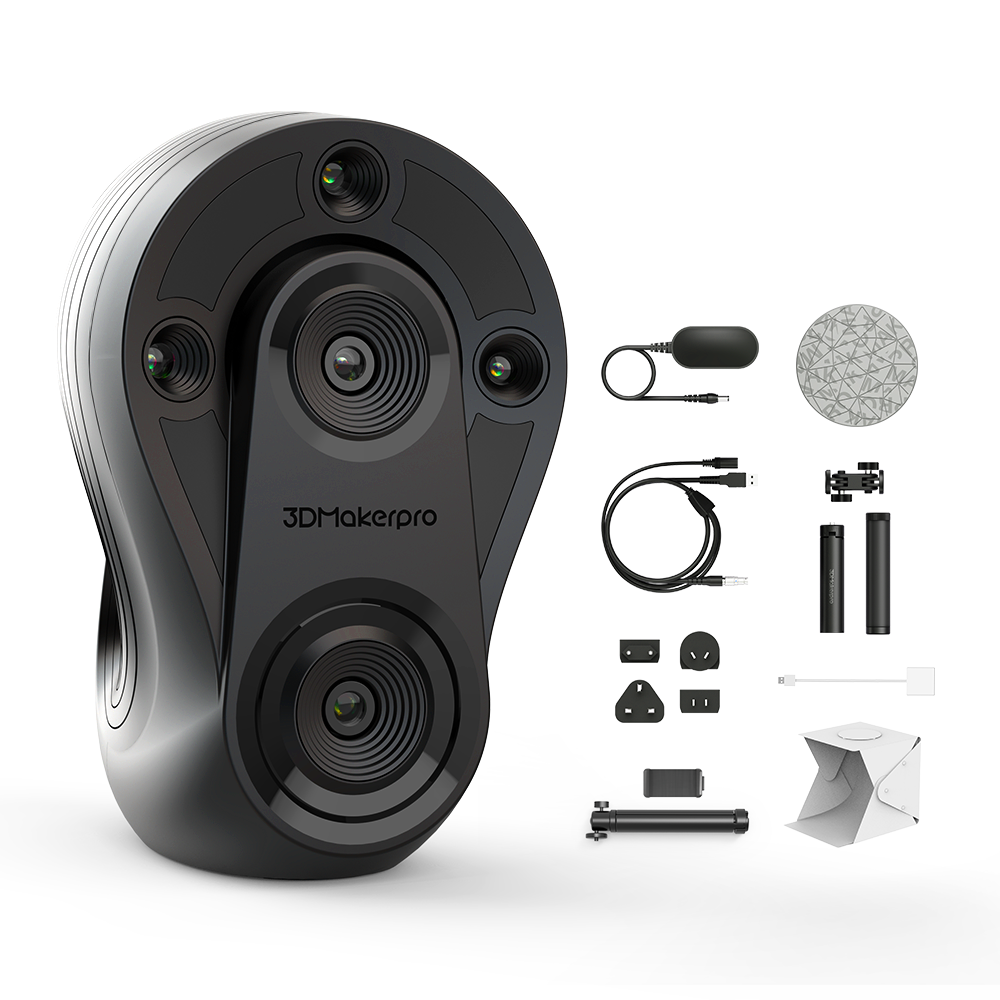




Whale Skaner 3D