¿Qué es la tecnología SLAM?
GOLPE (Localización y Mapeo Simultáneos) es una tecnología clave en robótica y visión artificial que utiliza datos de diversos sensores, como cámaras, LIDAR e IMU, para identificar características del entorno. Esta capacidad permite que un dispositivo navegue de forma autónoma sin conocimiento previo del área, a la vez que mapea dicho entorno.
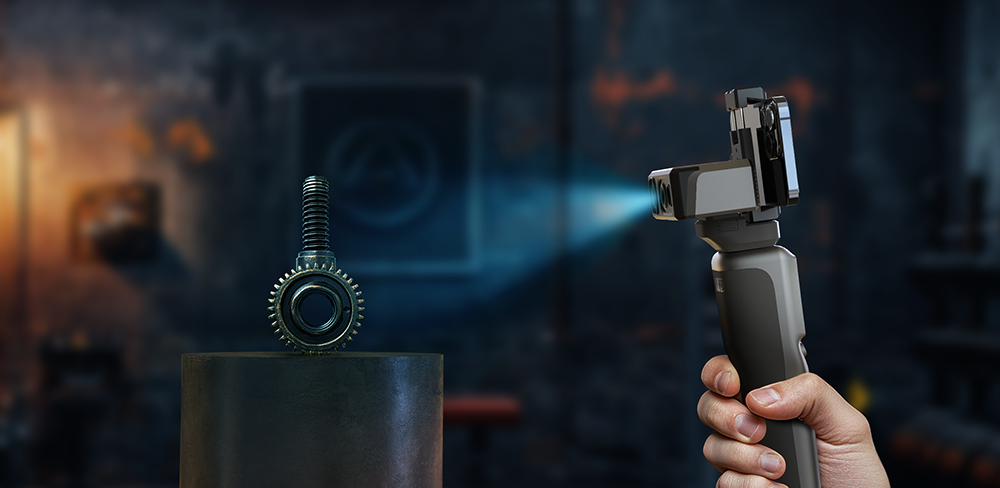
El funcionamiento de SLAM implica varios pasos clave. Primero, el dispositivo captura datos de sensores para reconocer las características de su entorno. A continuación, algoritmos procesan estos datos para estimar la trayectoria del dispositivo mientras construyen un mapa. Un componente crítico de este proceso es "Cierre de bucle" Este sistema detecta cuándo el dispositivo ha vuelto a visitar un área previamente mapeada, lo que le permite corregir cualquier error acumulado tanto en el mapa como en la localización. Al refinar continuamente tanto el mapa como la posición del dispositivo, SLAM facilita una navegación robusta en entornos dinámicos y complejos, lo que lo convierte en un componente esencial de los sistemas autónomos modernos. (La ruta morada representa la ruta de escaneo y el punto es el punto de inicio y el punto final).
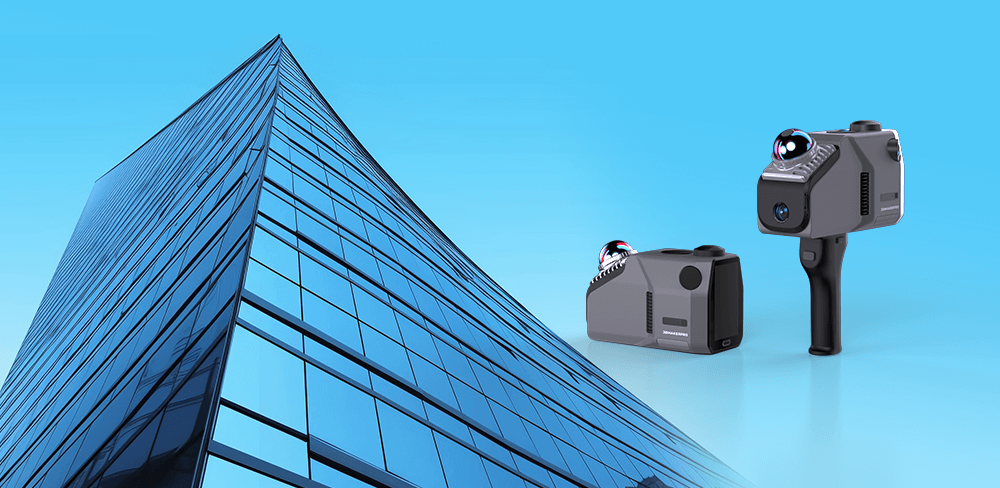
Eagle utiliza tecnología SLAM
El Escáner lidar Eagle La serie está diseñada para integrar a la perfección capacidades avanzadas de imagen y mapeo, especialmente mediante el uso de la tecnología SLAM. Disponible en dos modelos: el Eagle Max, con cuatro de 48 MP Cámaras HD y la Eagle estándar, equipada con una cámara HD de 48 MP cámara—ambas son capaces de producir imágenes impresionantes 8K HDR Imágenes panorámicas de ultraalta definición. El Eagle Max ofrece opciones versátiles de adquisición multivista, incluyendo en primera persona, cenital y... 45° perspectivas, lo que permite una recopilación eficaz de datos en una variedad de entornos y mejora la adaptabilidad durante las operaciones de escaneo.
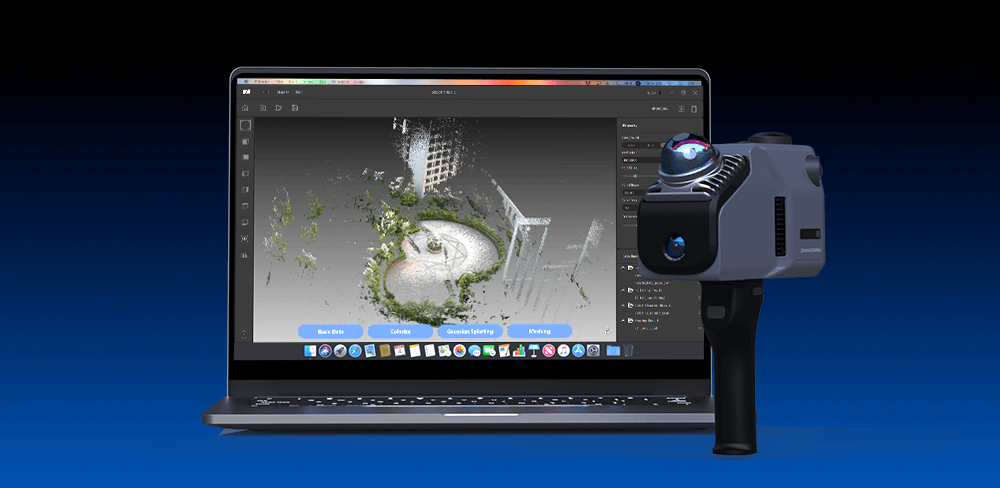
Gracias a la tecnología SLAM, la serie Eagle destaca en la construcción de modelos ambientales detallados mediante localización y mapeo en tiempo real. Al identificar y aprovechar las características ambientales, estos escáneres pueden navegar por espacios complejos con múltiples rutas y elevaciones variables, lo que garantiza un modelado preciso incluso en condiciones difíciles. Con niveles de precisión de hasta 2 cm a 10 metros, 3 cm a 20 metros y 5 cm a 40 metrosLa serie Eagle es especialmente adecuada para aplicaciones de diseño y mapeo que requieren un alto grado de precisión.
Además de sus impresionantes capacidades de imagen y cartografía, la serie Eagle incorpora datos GPS para el posicionamiento de coordenadas tanto absolutas como relativas. Esta integración permite a los usuarios combinar los resultados del escaneo con mapas existentes, proporcionando una visión completa y coherente del entorno escaneado. Al aprovechar la potencia de la tecnología SLAM, la serie de escáneres Eagle LiDAR no solo captura imágenes de alta calidad, sino que también garantiza datos fiables y precisos para una navegación y un modelado eficaces en entornos diversos y complejos.
Ventajas de la tecnología SLAM
1. Navegación autónoma
SLAM empodera Escáner LiDAR Eagle Navegar por entornos desconocidos sin necesidad de mapas preexistentes. Esto es especialmente beneficioso en escenarios como operaciones de búsqueda y rescate o misiones exploratorias, donde el entorno puede ser impredecible. La capacidad de operar de forma autónoma mejora la eficiencia y la seguridad, ya que los dispositivos pueden tomar decisiones en tiempo real basándose en su entorno.
2. Mapeo en tiempo real
Una de las características destacadas de SLAM es su capacidad para crear mapas sobre la marcha. A medida que el Eagle se desplaza, recopila continuamente datos de sus sensores, como cámaras y LIDAR, y procesa esta información para actualizar el mapa en tiempo real. Esto es crucial en entornos dinámicos donde los obstáculos pueden cambiar o pueden aparecer nuevas características, lo que permite al dispositivo adaptar sus estrategias de navegación en consecuencia.
3. Alta precisión
La tecnología SLAM emplea algoritmos sofisticados para lograr una precisión excepcional en el posicionamiento y el mapeo. Al aprovechar las técnicas de fusión de sensores, SLAM combina eficazmente los datos de múltiples sensores para minimizar los errores. El escáner lidar Eagle proporciona una precisión impresionante de hasta 2 centímetros, lo que es especialmente crucial en aplicaciones como el mapeo de edificios, donde el modelado espacial preciso es esencial para una planificación y ejecución efectivas.
4. Confiabilidad en entornos complejos
SLAM está diseñado para gestionar las complejidades de entornos reales, incluyendo espacios interiores con diseños complejos y exteriores con terrenos variados. Puede navegar por zonas congestionadas, como habitaciones abarrotadas o bosques densos, reconociendo elementos como paredes, muebles y puntos de referencia naturales. Además, SLAM puede gestionar múltiples niveles y cambios dinámicos en el entorno, como objetos u obstáculos en movimiento.
5. Rentabilidad
Los métodos tradicionales de mapeo suelen requerir mucha mano de obra e infraestructura, como levantamientos topográficos previos o equipos costosos. SLAM reduce estos costos al permitir que los dispositivos recopilen y mapeen su entorno de forma autónoma. Esto no solo reduce los gastos operativos, sino que también acelera el proceso de recopilación de datos, lo que permite una entrega más rápida de los proyectos. Nuestra serie Eagle tiene un precio de alrededor de $2,000, lo cual resulta muy rentable en comparación con el precio de mercado de $4,000¡Reserva y obtén hasta un 50% de descuento!
6. Integración con otras tecnologías
El Escáneres lidar Eagle Utilice SLAM junto con GPS, Unidades de Medición Inercial (IMU) y sistemas de visión artificial. En exteriores, el GPS proporciona datos de posicionamiento absoluto, mientras que SLAM supervisa la cartografía y la navegación locales. Esta integración mejora la precisión y la fiabilidad del sistema, permitiéndole posicionarse con precisión al escanear cada ubicación.
7. Flexibilidad y escalabilidad
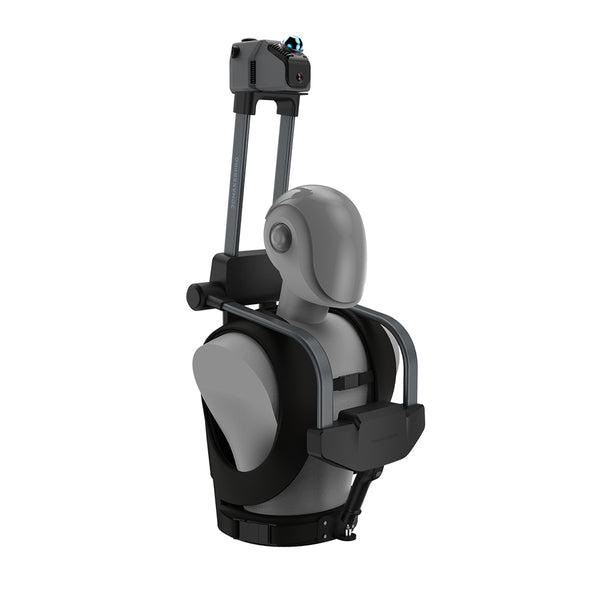
Los sistemas SLAM pueden diseñarse para funcionar con una amplia gama de expansiones o sensores, lo que los hace adaptables a diferentes aplicaciones y entornos. Eagle permite instalar un trípode manual para recopilar información espacial en puntos fijos, añadir un soporte de techo para automóvil para fijarlo al vehículo y capturar imágenes del paisaje urbano a voluntad; o usar un kit de mochila para recopilar datos en la espalda, que puede usarse para ejercicios y recopilación sincronizada; o usar un kit de bicicleta para montarlo en la bicicleta. También puede usar el módulo de antena y señal RTK para adquirir datos GPS para topografía y cartografía.
8. Varias aplicaciones
La tecnología SLAM tiene una amplia gama de aplicaciones en numerosos sectores, como la realidad aumentada (RA) y la realidad virtual (RV), el mapeo de campos agrícolas, la monitorización del transporte, la topografía de la construcción, la monitorización ambiental y la domótica, entre otros. Su versatilidad y eficacia la convierten en una herramienta valiosa para mejorar la eficiencia operativa y ofrecer soluciones innovadoras en estos sectores.

Datos de la colección
Primero, instale el mango del Eagle alineando la hebilla metálica del mango con la hebilla metálica de la máquina. Esto facilitará el escaneo. A continuación, encienda la máquina manteniendo presionado el botón de encendido/apagado en la pantalla durante aproximadamente... 6 segundos (El mismo proceso se aplica para apagarlo). El símbolo del sol en la esquina inferior derecha permite seleccionar los modos interior y exterior, así como ajustar el brillo y la exposición para lograr mejores efectos de modelo en el procesamiento posterior.
Haga clic en el botón "Escanear" y asigne un nombre al proyecto que desea escanear. Si se encuentra al aire libre, puede activar el GPS; sin embargo, esta función no está disponible en interiores. Normalmente recomendamos seleccionar "Escaneo continuo". Al encender el dispositivo por primera vez, el sistema sincronizará automáticamente la cámara y el láser durante aproximadamente... 30 segundosUna vez completada la sincronización, el botón "Escanear" en la parte inferior se volverá azul. Haga clic en este botón para comenzar el escaneo.
Durante el proceso de adquisición, la cámara de cuatro direcciones capturará automáticamente imágenes con una resolución de 4000x3000 píxeles, a una velocidad de una foto por segundo. Durante el proceso de escaneo, la información recopilada sobre la nube de puntos láser y la vista de la cámara se mostrará en tiempo real. Las tres imágenes en la parte superior de la pantalla representan diferentes ángulos de visión de la nube de puntos, que el usuario puede alternar: vista en primera persona, vista aérea y 45 grados Vista aérea. El temporizador en el área roja de la parte inferior de la pantalla indica la duración de la recopilación de datos.
Sostenga el Escáner LiDAR Eagle Manténgase firme a lo largo del área que desea escanear, manteniendo una velocidad constante. Una vez finalizada la recopilación de datos, apunte la cámara hacia el punto de inicio. No es necesario caminar de regreso; simplemente asegúrese de que la cámara esté apuntando a la posición inicial. Una pantalla de 0° Indica que ha regresado al punto de partida. Este proceso es lo que antes llamábamos "Bucle Cerrado". Una vez completado el bucle cerrado, haga clic en el botón de tiempo para finalizar el escaneo y, finalmente, haga clic en el botón "Guardar" para finalizar el proyecto.