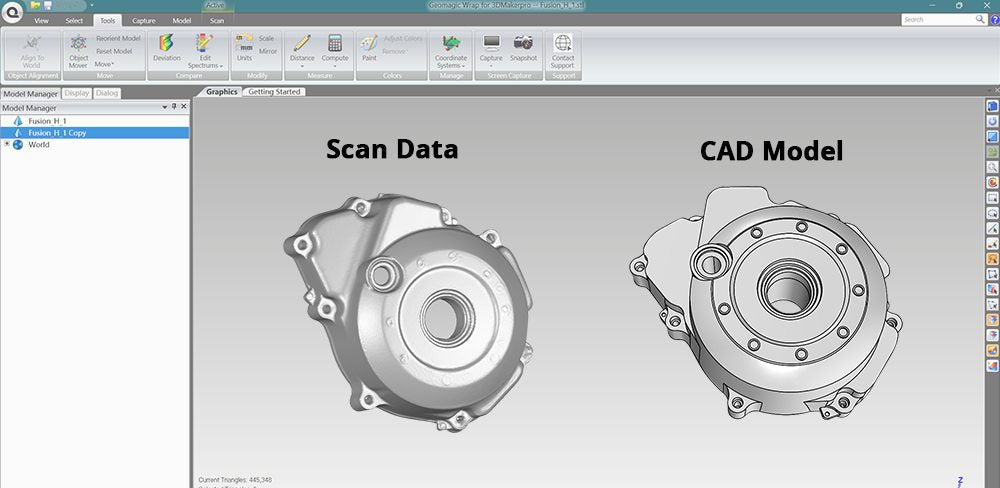
Che cosa è il Reverse Engineering
Il reverse engineering è un processo di imitazione tecnica che prevede la deduzione e la derivazione degli elementi di progettazione della struttura organizzativa e delle specifiche funzionali di un prodotto. Ciò si ottiene attraverso l'analisi inversa e l'esame dell'oggetto, con l'obiettivo di creare un prodotto con aspetto e funzionalità simili. L'obiettivo principale del reverse engineering è estrarre i principi di progettazione direttamente dall'analisi di un prodotto finito, in particolare quando le informazioni di produzione non sono prontamente disponibili. Questa pratica ha avuto origine nell'analisi di hardware sia in ambito commerciale che militare.
Che cosa è la scansione 3D
La scansione 3D è una tecnica senza contatto che utilizza laser per acquisire le caratteristiche superficiali e le dimensioni di un oggetto, generando un modello digitale al computer. Questa tecnologia trova applicazioni in diversi settori, tra cui la produzione di prodotti, la medicina e l'assistenza sanitaria, la conservazione del patrimonio culturale e il reverse engineering.
La relazione tra loro
Con l'avvento della tecnologia di scansione 3D, il reverse engineering è diventato notevolmente più semplice. Questa tecnologia impiega raggi laser per catturare con precisione la complessa forma tridimensionale e i dati spaziali di un oggetto, generando una densa nuvola di punti che forma un modello digitale 3D. Un software di scansione specializzato può quindi misurare e analizzare questi dati, consentendo una comprensione più approfondita del design dell'oggetto originale, che può essere replicato o migliorato.
Come realizzare il reverse engineering
① Preparazione del progetto
Prima di iniziare il progetto, è fondamentale determinare il modello e lo scanner che si intende utilizzare, poiché questo può influire sul successo. Se il modello è nero, rosso o di un altro colore scuro, è consigliabile scegliere uno scanner che gestisca efficacemente queste condizioni oppure utilizzare uno spray per la scansione per mitigare i problemi di riflessione. scanner eccelle in diverse dimensioni e precisioni, quindi seleziona quello più adatto e presta attenzione ai suoi parametri.
② Avvia la scansione
Maneggiare lo scanner con fermezza e catturare tutte le caratteristiche del modello per generare un modello digitale completo. Sebbene una singola scansione sia l'ideale, anche più scansioni possono essere eseguite correttamente, se allineate correttamente.
③ Elaborazione di nuvole di punti
Utilizzare il software di scansione, Studio JM Fornito con lo scanner per eseguire processi di base come allineamento, rimozione del rumore, fusione, rimozione di parti mobili e riparazione di spazi vuoti. In genere, il modello finale viene esportato come file .OBJ, .PLY, .STL e .RSCAN.
④ Esportazione nel modello CAD
Importa il tuo file .obj in Geomagic Wrap per 3DMakerpro Per ulteriori elaborazioni. Le funzioni comuni includono texture mapping, cleanup, costruzione di mesh HD, rilevamento dei contorni e creazione di cilindri. Una volta completato, salva il tuo lavoro in formati come .IGES, .WRP, .PLY, .STL, .OBJ.
⑤ Verificare e confrontare
Importa il tuo modello CAD in un software di slicing per prepararlo alla stampa 3D. Dopo la produzione, confronta il prodotto finale con l'originale e analizza i punti di forza e di debolezza per migliorare i progetti futuri. Un reverse engineering efficace può portare alla sostituzione di componenti vecchi o danneggiati, o persino all'invenzione di accessori avanzati, il che è significativo sia per la produzione che per la conservazione del patrimonio culturale.

Storie di successo
1. Tutorial Geomagic Wrap: reverse engineering ed esportazione in CAD
2. Scansione 3D in Geomagic Wrap con impostazioni CMM portatili
3. Geomagic Wrap: come creare un piano di ritaglio
Vantaggi della scansione 3D nel reverse engineering
A) Alta precisione:
La tecnologia di scansione 3D cattura migliaia di punti dati sulla superficie di un oggetto, producendo un modello digitale estremamente accurato. Questo livello di precisione è fondamentale per le applicazioni che richiedono tolleranze ristrette, come i componenti automobilistici o il settore medico-odontoiatrico, dove anche piccole deviazioni possono causare problemi di prestazioni.
B) Velocità ed efficienza:
Le capacità di raccolta rapida dei dati di scanner 3D consentono la cattura completa di geometrie complesse in una frazione del tempo necessario con tecniche di misurazione tradizionali, come calibri o rilievi manuali. Questa efficienza accelera il processo di reverse engineering, consentendo tempi di consegna più rapidi per lo sviluppo del prodotto.
C) Non distruttivo:
Essendo un metodo senza contatto, la scansione 3D non interagisce fisicamente con l'oggetto da scansionare. Questo è particolarmente vantaggioso per oggetti delicati, come reperti storici o prototipi fragili, dove qualsiasi manipolazione potrebbe danneggiarli. La capacità di raccogliere dati senza alterare l'oggetto originale è preziosa negli interventi di conservazione e restauro.
D) Versatilità:
La scansione 3D è applicabile in un'ampia gamma di settori, tra cui la produzione, la sanità, l'archeologia e la progettazione automobilistica. Questa versatilità consente alle organizzazioni di utilizzare la stessa tecnologia per diversi scopi, come il controllo qualità, la modellazione medica e la documentazione del patrimonio culturale, rendendola uno strumento poliedrico per il reverse engineering.
E) Conveniente:
Riducendo il tempo e la manodopera coinvolti nei processi di misurazione e modellazione, Scansione 3D può portare a significativi risparmi sui costi. Le organizzazioni possono semplificare i flussi di lavoro, ridurre al minimo gli errori e aumentare la produttività, con conseguente riduzione dei costi di produzione e un più rapido ingresso sul mercato di nuovi prodotti.