Einführung
Die Forensik entwickelt sich ständig weiter und integriert fortschrittliche Technologien, um die Genauigkeit und Effizienz von Ermittlungen zu verbessern. Eine dieser Innovationen ist Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR), eine leistungsstarke räumliche Scantechnologie, die in der Forensik wichtige Anwendungen findet. Dieser Blog untersucht, wie LiDAR-Scanner, insbesondere die Eagle LiDAR-Scanner, revolutionieren Tatortuntersuchungen, archäologische Studien und Umweltverträglichkeitsprüfungen und verändern letztlich die Landschaft der forensischen Analyse.
Was ist LiDAR?
LiDAR ist ein Fernerkundungsverfahren, das gepulste Laserstrahlen zur Entfernungsmessung nutzt. Durch das Aussenden dieser Strahlen und die Berechnung der Rücklaufzeit erstellt LiDAR präzise, dreidimensionale Karten des gescannten Gebiets. Diese Technologie kann Vegetation und andere Hindernisse durchdringen und ist daher besonders in dichten Umgebungen nützlich, in denen herkömmliche Vermessungsmethoden an ihre Grenzen stoßen. Die resultierenden Daten sind nicht nur präzise, sondern auch detailreich und bieten einen umfassenden Überblick über die Umgebung.
Anwendungen in der Forensik
1. Rekonstruktion des Tatorts
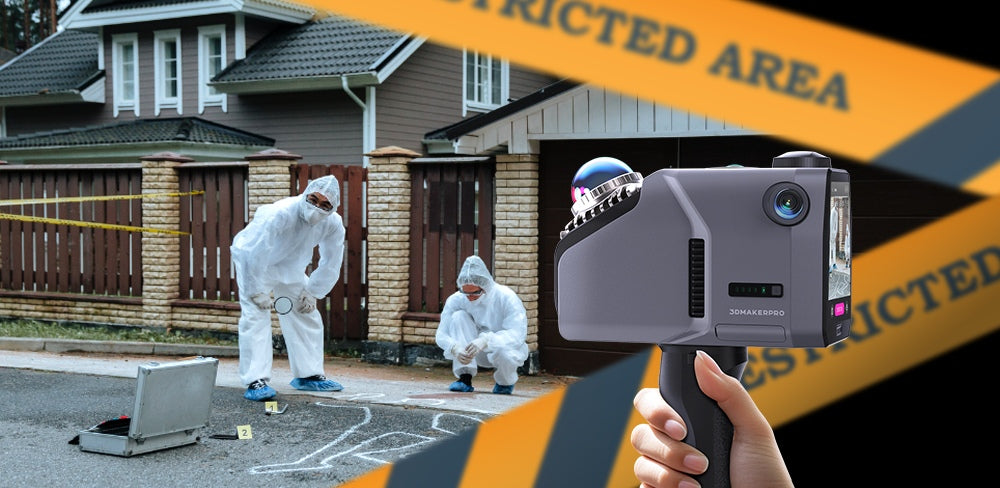
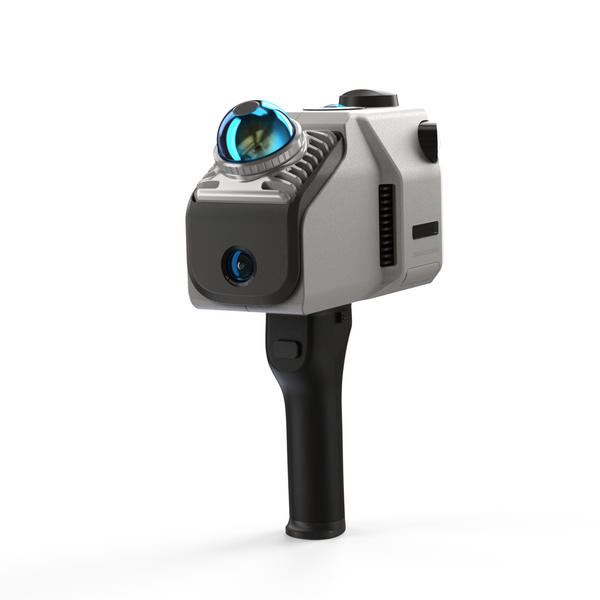
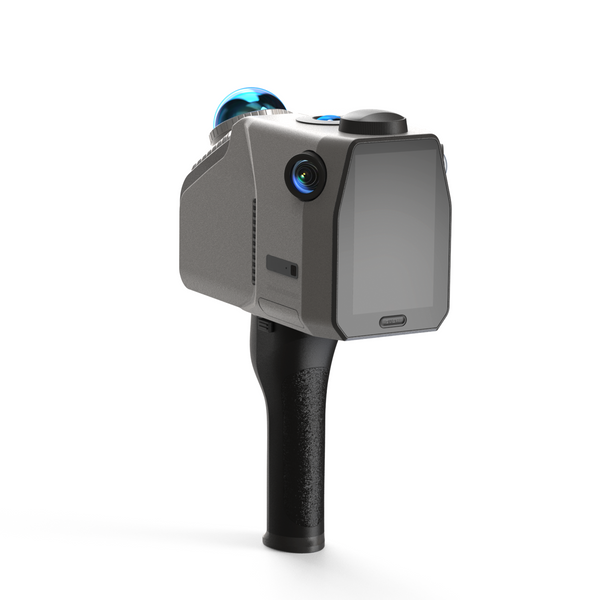
LiDAR-Scanner sind für die Untersuchung von Tatorten von unschätzbarem Wert. Die Eagle LiDAR-Scanner erfasst detaillierte Geländedaten und erzeugt mit seinem fortschrittlichen 48-Megapixel-HD-Kamerasystem atemberaubende, ultrascharfe 8K-HDR-Panoramabilder. Diese branchenführende Bildgebungsfunktion liefert farbgenaue 3D-Daten, die für die Visualisierung räumlicher Beziehungen zwischen Beweismitteln und die realistische Rekonstruktion von Tatorten entscheidend sind. Diese Genauigkeit hilft Ermittlern, die Dynamik von Verbrechen zu verstehen, einschließlich der Standorte von Verdächtigen und Opfern. Sobald der Scan abgeschlossen ist, kann er in verschiedenen Formaten exportiert werden, z. B. als 3D-Farbpunktwolke (PLY), 3D-Gaussian Splatting (PLY), 3D-Farbpolygonmodell (OBJ) und 3D-Panoramatourdaten (OBJ). Dies ermöglicht eine immersive Analyse und Simulation des Tatorts, die auch als Beweismittel vor Gericht verwendet werden kann.
2. Beweisdokumentation
Traditionelle Methoden der Tatortdokumentation, wie Fotografie oder Skizzen, können subjektiv und fehleranfällig sein. Die Adler Die hohe Genauigkeit (2 cm auf 10 m) stellt sicher, dass selbst kleinste Details für eine gründliche Analyse erhalten bleiben. Die 8K-HD-Bildgebung bringt Beweise schärfer in den Fokus, maximiert die Klarheit und dokumentiert wichtige Informationen. Darüber hinaus verbessert die Fähigkeit, einen 150 x 150 m großen Tatort in weniger als fünf Minuten zu scannen, die Effizienz der Beweisaufnahme erheblich, sodass sich Forensikteams auf die Analyse statt auf die Datenerfassung konzentrieren können. Diese umfassende Dokumentation ist eine wertvolle Ressource für Ermittlungen und Gerichtsverfahren.
3. Archäologische Untersuchungen
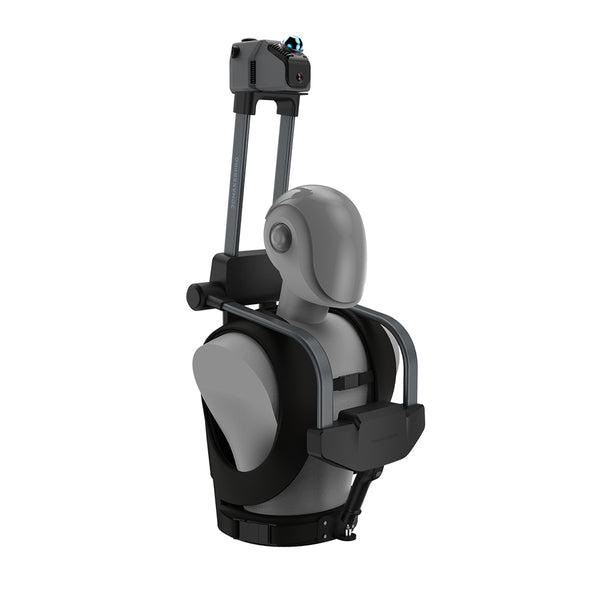
LiDAR hat bedeutende Beiträge zur forensischen Archäologie geleistet, insbesondere bei der Ortung vergrabener Beweise oder geheimer Gräber. Die Hawkeye-Scanner nutzen die SLAM-Technologie (Simultaneous Localization and Map Building) zur Erstellung von Umweltmodellen, die es Ermittlern ermöglichen, unterirdische Strukturen ohne invasive Ausgrabungen zu visualisieren. Dieser nicht-invasive Ansatz ist entscheidend für die Erhaltung der Integrität archäologischer Stätten. Darüber hinaus bieten die verschiedenen Aufnahmeoptionen (Egoperspektive, Draufsicht und 45-Grad-Draufsicht) Flexibilität für die gründliche Erkundung komplexer Szenen. Die Adler kann auch auf verschiedenen Fahrzeugen wie Fahrrädern, Autos und Drohnen montiert werden, wodurch seine Fähigkeit verbessert wird, unter unterschiedlichen Bedingungen ein genaues Scannen zu erreichen.
4. Umweltverträglichkeitsprüfung
Forensiker müssen oft die Umgebung eines Tatorts beurteilen. Die Eagle LiDAR-Scanner Kartiert Landschaften und Merkmale mit einem Scanradius von bis zu 70 Metern und liefert wichtige Informationen darüber, wie Umweltfaktoren den Fall beeinflusst haben könnten. Mit einem RTK-Modul, das GPS-Daten für die absolute und relative Positionierung integriert, können umfassende Umgebungsscans im Innen- und Außenbereich durchgeführt werden, um zu analysieren, wie natürliche Faktoren im Laufe der Zeit Beweise beeinflusst haben könnten.
Vorteile von LiDAR in der Forensik
Hohe Präzision: Der Eagle Scanner Genauigkeit – 2 cm bei 10 m, 3 cm bei 20 m und 5 cm bei 40 m – gewährleistet eine zuverlässige Datenerfassung und eignet sich daher für Anwendungen, die eine hohe Präzision erfordern.
Nicht-invasiv: Die Möglichkeit, Daten zu sammeln, ohne den Tatort zu stören, minimiert die Kontamination und bewahrt Beweise für zukünftige Untersuchungen.
Schnelle Datenerfassung: Mit Bewegungserfassungsgeschwindigkeiten von bis zu 20 km/h kann der Eagle Scanner große Bereiche schnell abdecken und so effiziente Untersuchungen insbesondere in zeitkritischen Fällen ermöglichen.
Verbesserte Visualisierung: Die 8K-HDR-Bildgebung ermöglicht klare visuelle Darstellungen des Tatorts und erleichtert so die Kommunikation mit Geschworenen, Beteiligten und der Öffentlichkeit. Diese detaillierten Bilder können bei Präsentationen und Gerichtsverfahren von entscheidender Bedeutung sein.
Trotz seiner vielen Vorteile bringt LiDAR auch Herausforderungen mit sich. Für den effektiven Einsatz der Technologie sind spezielle Schulungen und Fachwissen sowie ein tiefes Verständnis forensischer Prinzipien zur präzisen Dateninterpretation erforderlich. Zudem kann die finanzielle Investition in diese fortschrittliche Technologie für kleinere Behörden oder Organisationen eine Hürde darstellen. Das Eagle-Gerät ist jedoch benutzerfreundlich und bietet ausführliche Tutorial-Videos und Artikel, die auch Anfängern den Einstieg erleichtern. Darüber hinaus ist es im Vergleich zu vielen anderen LiDAR-Scannern auf dem Markt kostengünstig.
Fazit
LiDAR-Raumscanner, insbesondere die Eagle LiDAR-Scanner, revolutionieren die Forensik, indem sie fortschrittliche Werkzeuge für die Rekonstruktion von Tatorten, die Dokumentation von Beweismitteln und Umweltverträglichkeitsprüfungen bereitstellen. Mit seiner hochauflösenden Bildgebung, Präzision und Effizienz verbessert der Eagle Scanner die Genauigkeit und Zuverlässigkeit forensischer Analysen. Mit dem weiteren technologischen Fortschritt wird die Integration von LiDAR in forensische Untersuchungen voraussichtlich noch weiter an Bedeutung gewinnen. So wird sichergestellt, dass der Gerechtigkeit effektiv Genüge getan wird und gleichzeitig die wissenschaftliche Integrität der Ermittlungen gewahrt bleibt. Die Nutzung solcher Innovationen ist für die Weiterentwicklung des Fachgebiets von entscheidender Bedeutung und ebnet den Weg für robustere und transparentere forensische Verfahren.