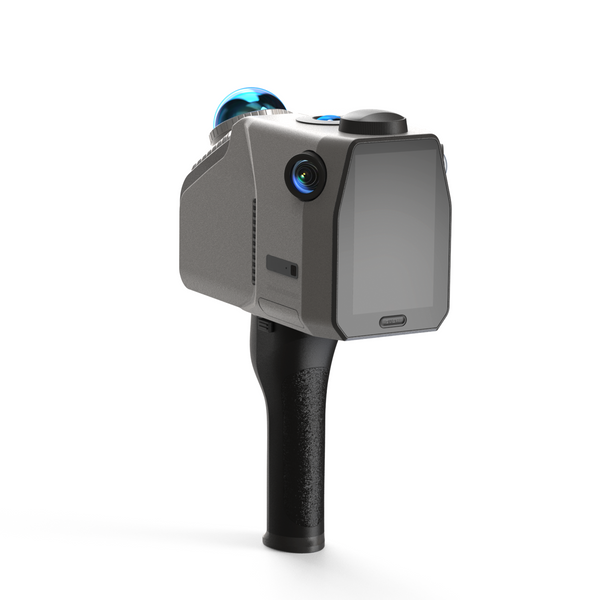
En el campo de la topografía y la cartografía, en rápida evolución, la integración de escáneres de radar espacial en drones representa un avance monumental. Esta innovadora tecnología no solo mejora la capacidad de recopilación de datos, sino que también abre nuevas vías de aplicación en diversas industrias. En esta entrada del blog, exploraremos cómo los escáneres de radar espacial instalados en drones, en particular... Escáner LiDAR Eagle, están transformando las operaciones cartográficas y los innumerables beneficios que aportan a los profesionales del campo.
¿Qué es un escáner de radar espacial?
Un escáner de radar espacial utiliza tecnología de radar avanzada para capturar información detallada sobre la superficie terrestre y sus características. A diferencia de los sensores ópticos tradicionales, que se basan en la luz visible, el radar puede penetrar nubes, vegetación e incluso algunos tipos de suelo, lo que lo hace especialmente valioso en entornos con visibilidad limitada o difícil. Al combinarse con la tecnología de drones, los escáneres de radar espacial pueden cubrir grandes áreas de forma rápida y eficiente, proporcionando datos de alta resolución para cartografía y análisis. Esta capacidad es especialmente útil en zonas remotas o inaccesibles donde los métodos de topografía convencionales pueden resultar insuficientes.
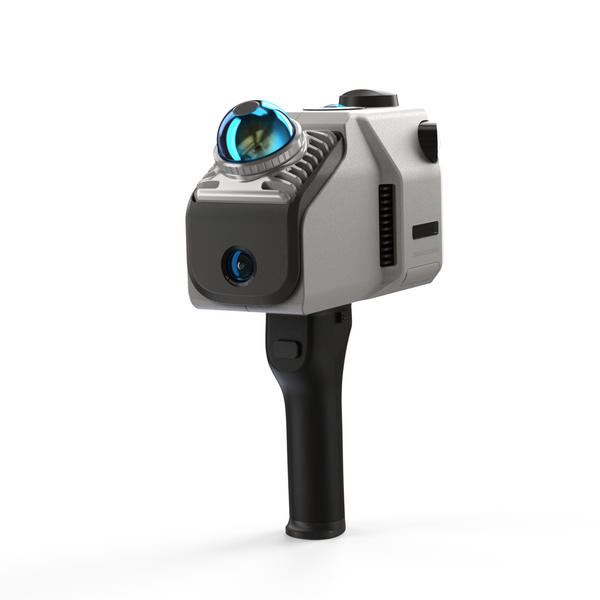
El escáner LiDAR Eagle: una potente herramienta para la cartografía
El Escáner LiDAR Eagle ejemplifica cómo la tecnología de radar espacial puede mejorar las capacidades de los drones. Equipado con un 48MP Con su sistema de cámara de alta definición, el Eagle puede crear imágenes impresionantes. 8K Imágenes panorámicas HDR ultranítidas. Esta función de imagen líder en la industria garantiza que los usuarios reciban datos 3D con gran detalle y colores precisos, lo que convierte al Eagle en la opción ideal para aplicaciones que requieren alta resolución y una calidad de imagen excepcional.
Aplicaciones de los escáneres de radar espacial en operaciones cartográficas
1. Cartografía topográfica
Los escáneres de radar espacial, como el Eagle, son ideales para crear mapas topográficos complejos que representan la elevación y el relieve del terreno. Al capturar datos desde arriba, los drones equipados con el Eagle pueden generar modelos digitales de elevación (MDE) precisos, cruciales para la ingeniería civil, la planificación del uso del suelo y las evaluaciones ambientales. Estos mapas proporcionan información valiosa para el desarrollo de infraestructura, la gestión de recursos y la preparación ante desastres, garantizando una planificación precisa y con visión de futuro de los proyectos.
2. Evaluación del riesgo de inundaciones
En el clima actual, comprender los riesgos de inundaciones nunca ha sido más crucial. Águila Capacidad para soportar niveles de precisión de 2 cm a 10 m, 3 cm a 20 m y 5 cm a 40 m Permite proporcionar datos fiables en zonas propensas a inundaciones. Esta precisión permite a los urbanistas y a las agencias de gestión de desastres identificar regiones vulnerables e implementar estrategias de mitigación eficaces, mejorando así la resiliencia de las comunidades ante las inundaciones. Al analizar datos históricos junto con evaluaciones actuales, las agencias pueden prepararse mejor ante fenómenos meteorológicos extremos, salvando vidas y reduciendo pérdidas económicas.
3. Monitoreo Agrícola
Los agricultores y los expertos agrícolas pueden beneficiarse significativamente de la tecnología de radar espacial. El uso de drones equipados con... ÁguilaPueden monitorear la salud de los cultivos, evaluar los niveles de humedad del suelo y detectar problemas de riego. La capacidad de escaneo de escenas extensas, con un radio de escaneo único de hasta 70 metros y la capacidad de cubrir una 150 m x 150 m El radar, que permite monitorear un área extensa en menos de cinco minutos, permite un monitoreo eficiente de campos extensos. Estos datos ayudan a optimizar las prácticas agrícolas, mejorar el rendimiento y gestionar los recursos de forma más eficaz. Además, el radar puede identificar el estrés de los cultivos antes de que se manifieste visualmente, lo que permite intervenciones oportunas que mejoran la productividad y la sostenibilidad.
4. Inspección de infraestructura
Drones equipados con el Escáner LiDAR Eagle Puede realizar inspecciones de infraestructuras de difícil acceso, como puentes, líneas eléctricas y tuberías. La capacidad de recopilar datos estructurales detallados sin necesidad de andamios ni inspección manual reduce el tiempo de inactividad y aumenta la seguridad. Las capacidades de captura multipunto del Eagle ofrecen tres opciones de visualización distintas: en primera persona, desde arriba y desde un... 45 grados Perspectiva aérea, lo que permite a los inspectores evaluar las estructuras desde múltiples ángulos. Esta capacidad permite realizar mantenimiento y reparaciones oportunas, lo que ayuda a prevenir fallos catastróficos y a garantizar la integridad de la infraestructura crítica.
5. Monitoreo y conservación ambiental
Los escáneres de radar espacial desempeñan un papel crucial en el monitoreo de cambios ambientales, como la deforestación, la degradación del suelo y la pérdida de hábitat. Al capturar datos exhaustivos a lo largo del tiempo, los drones equipados con el Eagle pueden ayudar a los conservacionistas a monitorear la salud de los ecosistemas y evaluar el impacto de las actividades humanas. Águila Capacidad para construir modelos ambientales utilizando GOLPE (Localización y Mapeo Simultáneos) garantiza un modelado preciso de espacios interiores y entornos exteriores complejos, lo cual es vital para desarrollar estrategias para proteger los recursos naturales y promover la biodiversidad.
6. Planificación y desarrollo urbano
Los planificadores urbanos pueden aprovechar los datos de radar espacial para comprender las complejidades de los entornos urbanos. Águila La capacidad de proporcionar datos de alta precisión y su compatibilidad con múltiples formatos de salida (nube de puntos en color PLY, PNG+OBJ panorámico, etc.) permite a los planificadores crear modelos y simulaciones detallados. Al mapear el uso del suelo, las redes de transporte y la densidad de población, los planificadores pueden tomar decisiones informadas sobre futuros proyectos de desarrollo. La capacidad de visualizar el impacto de los desarrollos propuestos en los ecosistemas y comunidades existentes garantiza un crecimiento sostenible.
Ventajas de utilizar escáneres de radar espacial en drones
a) Eficiencia: Los drones equipados con escáneres de radar espacial pueden cubrir grandes áreas en una fracción del tiempo que tomarían los métodos de topografía tradicionales. Águila velocidad de captura de movimiento de hasta 20 kilómetros por hora Y las capacidades de escaneo rápido se traducen en ahorros de costos significativos y una finalización más rápida del proyecto.
b) Accesibilidad: Los drones pueden acceder a terrenos difíciles o peligrosos que pueden suponer un reto para el personal de tierra. Esta capacidad permite la recopilación exhaustiva de datos en zonas que, de otro modo, quedarían sin vigilancia, como laderas empinadas, bosques densos o regiones afectadas por desastres.
c) Datos de alta resolución: El águila 8K Las imágenes HDR proporcionan datos detallados y precisos, lo que permite a los profesionales tomar decisiones informadas basadas en información fiable. Estos datos de alta calidad son cruciales para generar información práctica que impulse una planificación y una gestión de recursos eficaces.
d) Recopilación de datos en tiempo real: La capacidad de recopilar y analizar datos en tiempo real permite una rápida toma de decisiones, especialmente importante en situaciones de respuesta a emergencias. Esta inmediatez puede marcar una diferencia significativa en la gestión de desastres, permitiendo evacuaciones oportunas y la asignación de recursos.
Conclusión
La integración de escáneres de radar espacial, en particular el Escáner LiDAR EagleEl uso de drones está revolucionando las operaciones cartográficas en diversos sectores. Desde la cartografía topográfica y la evaluación del riesgo de inundaciones hasta la monitorización agrícola y la inspección de infraestructuras, las aplicaciones de esta tecnología son amplias y de gran impacto. A medida que esta tecnología siga avanzando, podemos esperar ver usos aún más innovadores que mejorarán aún más nuestra capacidad para comprender y gestionar el mundo que nos rodea.